Liver disease
Advocate Health Care's team of liver specialists is here to help you with liver health management and provide the best care possible for liver disease. We use the latest testing and treatment options available to provide top-notch care for all types of liver disease.
Liver disease affects millions of people around the world. It can be caused by excessive alcohol consumption, viral infections, genetics and certain medications.
Types of liver disease
Your liver is a vital organ that plays a vital role in your overall health. It filters toxins from your blood, produces bile to aid in digestion, stores glucose for later use and metabolizes some nutrients and medications. However, it can be overworked and develop liver disease.
Some common types of liver disease include:
- Alcoholic liver disease (ALD): Caused by excessive alcohol consumption. ALD can lead to inflammation, fibrosis and cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis: A condition in which the liver becomes severely scarred and damaged. It can be caused by a range of factors, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), ALD and hepatitis.
- Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver caused by a virus, such as hepatitis A, B or C.
- Liver cancer: A rare but serious complication of chronic liver disease.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Caused by excess fat buildup in the liver, this is the most common type of liver disease in the United States.
Stages of liver damage stages
If not treated, damage from liver disease can progress through stages from moderate to severe, which may require a liver transplant if your liver disease is further advanced. The stages of liver damage include:
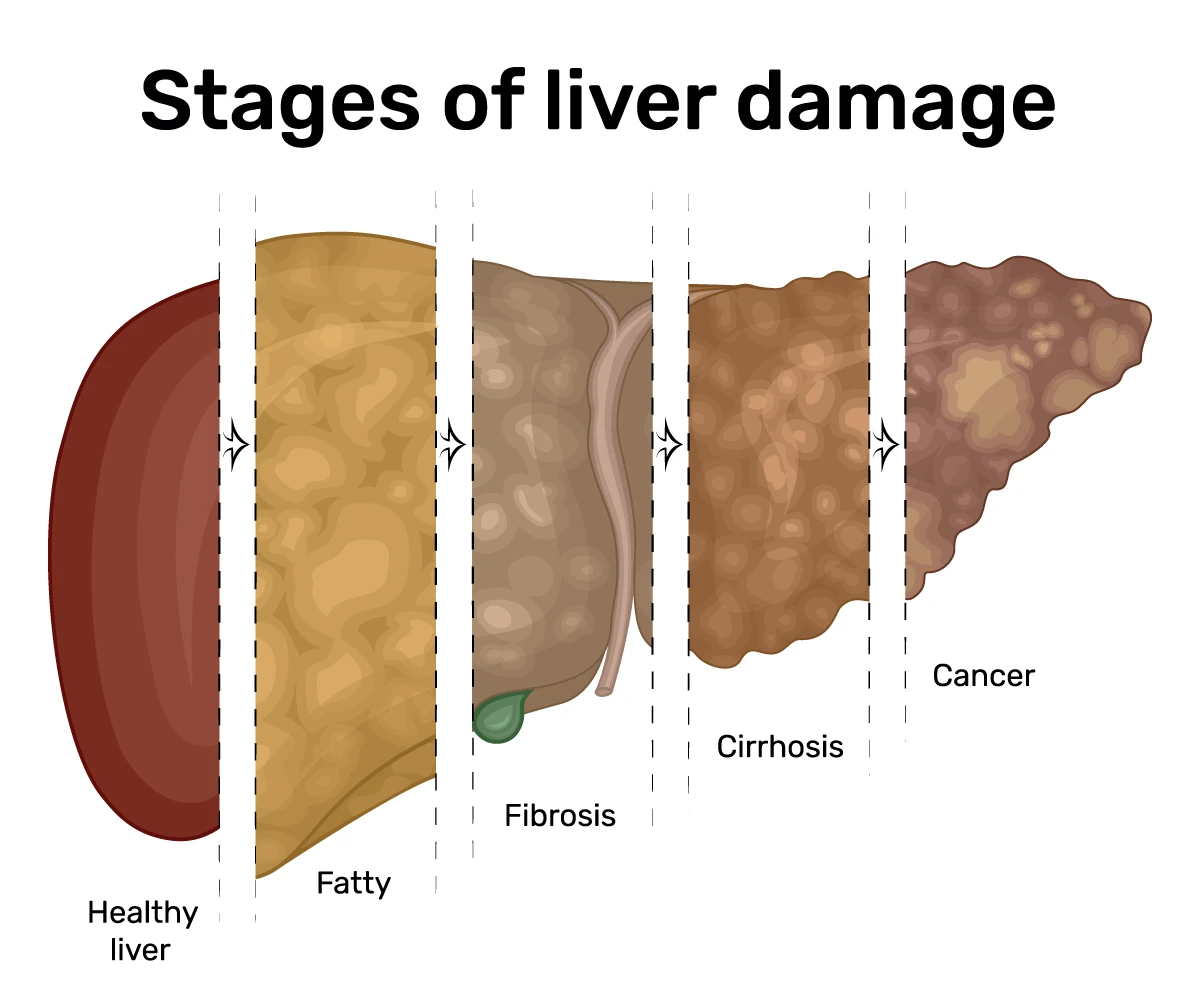
- Inflammation (fatty liver): This is the earliest stage of liver disease and not the same as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. It is characterized by inflammation or enlargment of the liver.
- Fibrosis: In this stage, the inflamed liver begins to develop scar tissue due to the accumulation of proteins, including collagen. It can affect liver function but may not cause any symptoms.
- Cirrhosis: This is a more advanced stage of liver disease in which the liver becomes severely scarred and permanently damaged. This makes it difficult for your liver to function. Symptoms may begin to be noticeable in this stage.
- End-stage liver disease (ESLD): This term is used to describe advanced cirrhosis or chronic liver failure. The only treatment for ESLD is a liver transplant.
- Cancer: While rare, liver cancer can develop in people with chronic liver disease caused by a viral infection or cirrhosis. Not everyone with cirrhosis will develop liver cancer. Men are more likely to develop liver cancer than women.
Causes of Liver Disease
Excessive alcohol consumption and viral infections such as hepatitis, are the leading causes of liver disease.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease develops when too much fat builds up in the liver. It’s often associated with obesity, diabetes and high cholesterol. Changes to your diet and losing weight can help reduce the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Certain medications, including those used to treat high cholesterol, amoxicillin combined with clavulanate, and anabolic steroids can damage the liver and lead to advanced liver disease. High doses of acetaminophen are also linked to liver disease.
Genetics and inherited conditions can also play a role in liver disease development.
Symptoms of liver disease
In the early stages of liver disease, you may not experience any symptoms. As the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
- Abdominal pain
- Dark urine
- Fatigue and weakness
- Jaundice (yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pale stool color
- Swelling in the legs and abdomen
See your doctor if you experience any of these symptoms.
Diagnosing and treating liver disease
To diagnose liver disease, your doctor will ask about your medical history and perform a physical exam. They may also order liver-function blood tests and a CT scan, MRI or ultrasound. If your doctor suspects you have liver cancer, they may order a liver biopsy.
Treatment depends on the type and severity of liver disease. In some cases, lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, quitting alcohol and eating a healthy diet, may be enough to improve liver function and prevent further damage. In other cases, medication or surgery, including needing a liver transplant, may be necessary.
Tips for preventing liver disease
There are several methods you can take to help prevent liver disease, including:
- Avoid exposure to toxins, including chemicals found in cleaning products
- Eat a healthy diet
- Get regular exercise
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Maintain a healthy weight
Talk with your doctor if you have any concerns about your liver health.
Get care
We help you live well. And we’re here for you in person and online.
