Esophageal varices
Esophageal varices are often a result of severe liver disease and may be life threatening. At Advocate Health Care, our expert team of esophageal varices specialists use the most up-to-date treatments and testing to diagnose and provide the best esophageal varices treatment possible.
Understanding esophageal varices
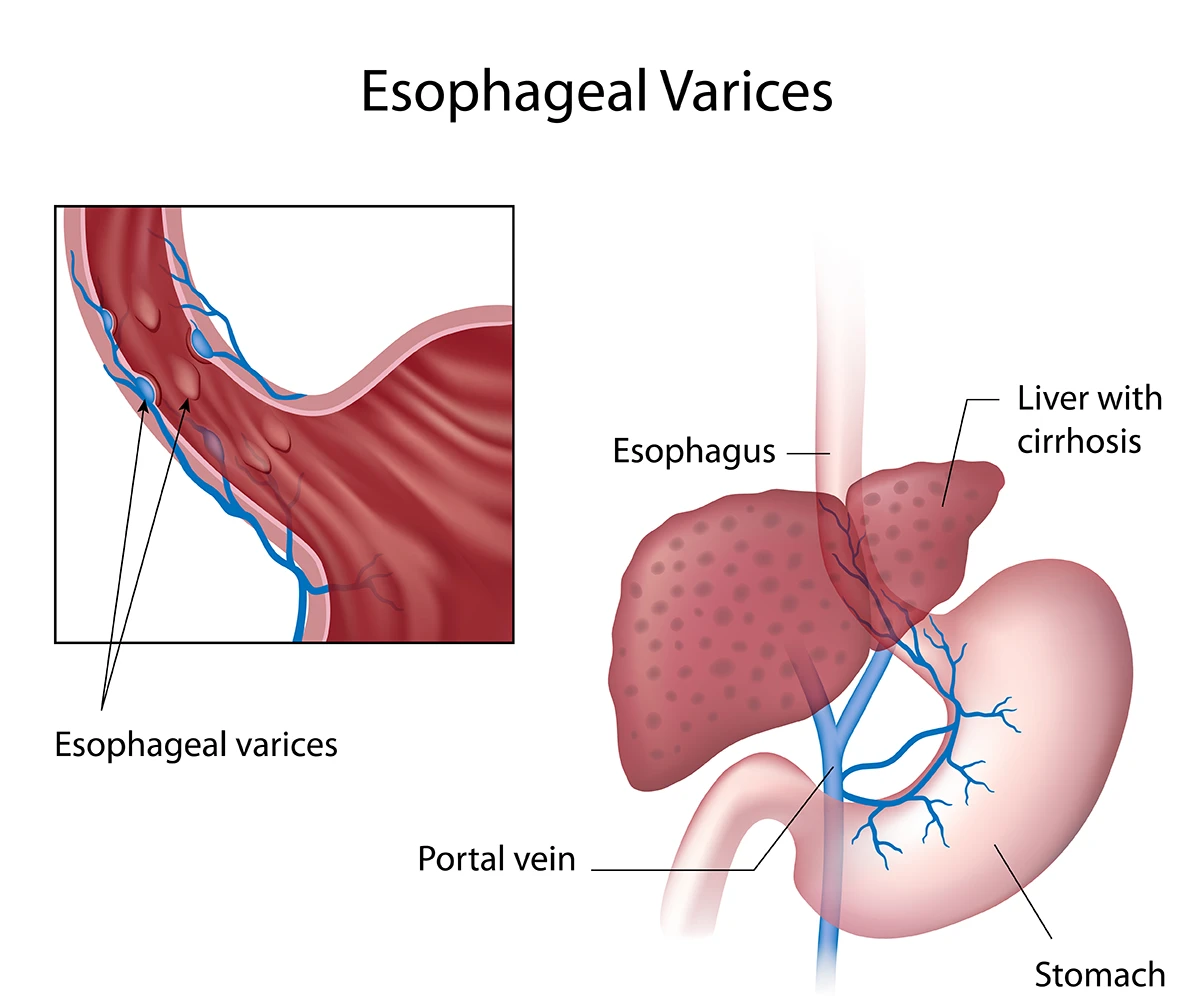
Esophageal varices are enlarged, swollen blood vessels that supply blood to the liver in the lower part of the esophagus, the tube connecting the throat to the stomach.
Esophageal varices develop because of blockages in these blood vessels that are connected to the liver. This causes blood to accumulate in the vessels, including in the esophagus, and find alternative routes to the liver.
To go around the blockages, blood travels through smaller vessels to get to the liver. These new paths increase the pressure in the vessels and could cause them to leak or rupture. A rupture of the vessel could cause life-threatening bleeding. If you are vomiting blood or see blood in your stool, call 911.
Esophageal varices causes & risk factors
Blood clots, liver disease and parasitic infections are common causes of esophageal varices. However, other causes such as cardiovascular disease and Type II diabetes may also lead to blockages of blood vessels in the esophagus.
Primary causes of esophageal varices
- Cirrhosis and liver diseases: Cirrhosis of the liver is the most common cause of esophageal varices. It is the scarring of the liver caused by diseases such as hepatitis C. This long-term, continuous damage may lead to liver failure.
- Blood pressure spike: A sudden rise in blood pressure in the portal venous system that supplies blood from the pancreas to the liver is another common cause of esophageal varices. This condition is known as portal hypertension and it often accompanies liver diseases.
Secondary causes of esophageal varices
- Blood clots (thrombosis): Blockages in the portal vein can cause blood to back up into other vessels, including those in the esophagus.
- Other causes: While rare, some infections, certain vascular conditions and tumors can also contribute to the formation of esophageal varices.
Risk factors for bleeding from esophageal varices
Many people who develop esophageal varices won’t have any bleeding. Your risk of bleeding increases due to:
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- A diet rich in fatty and fried foods
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Chronic hepatitis B or C infection
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Genetic factors
- Contributing conditions, such as schistosomiasis or Budd-Chiari syndrome, which can increase the risk of bleeding
Recognizing esophageal varices symptoms
Most of the time, you won’t have any symptoms from esophageal varices unless there is bleeding. If you do experience symptoms, they could include:
- Vomiting blood
- Black, tarry stools
- Signs of decreased blood volume (also called hypovolemic shock)
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Fluid buildup in the abdomen
- Confusion and slurred speech
If you have any of these symptoms, schedule an appointment with your Advocate gastrointestinal specialist as soon as possible.
Seek emergency care by calling 911 or going to the emergency department if you’re vomiting blood or notice blood in your stool.
Esophageal varices diagnosis & treatment options
If you have liver disease or cirrhosis, your Advocate specialist likely tests you for esophageal varices occasionally. If you’re showing symptoms of esophageal varices, your doctor will perform a physical exam, review your medical history and may order tests to determine the severity of your esophageal varices.
Some tests used to diagnose esophageal varices include endoscopy, CT scans and ultrasounds of the abdomen area. Your doctor may also use an ultrasound to view dilated veins.
Esophageal varices treatment
Advocate has advanced esophageal varices therapies and treatments available. Your doctor may recommend preventative treatment for better esophageal varices management or surgery to remove blockages.
One preventive treatment option includes prescription beta blockers to reduce blood pressure and the risk of bleeding. Your doctor may also recommend esophageal variceal banding , which is a procedure that places bands around the veins to prevent bleeding.
If you have a high risk of bleeding, your Advocate specialist may recommend surgery or a liver transplant for severe liver disease. A transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is the most common surgery performed on patients with esophageal varices. During a TIPS procedure, a shunt is created to redirect blood flow into the liver, which reduces portal hypertension.
Esophageal varices prevention
Keeping your liver healthy is essential to prevent esophageal varices. Even if you’ve been diagnosed with liver disease, the following strategies are recommended to improve liver health:
- Don’t drink alcohol: Alcohol is processed in the liver and adds more stress to it. If you have liver disease, your doctor may advise you to stop drinking alcohol completely.
- Eat a healthy diet: Eat a diet full of lean protein, fruits and vegetables and limit fatty foods.
- Limit your exposure to toxins: Your liver removes toxins from your body. Follow safety precautions and wear gloves when using household chemicals.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess body fat adds more stress on your liver. Obesity increases your risk of complications of cirrhosis.
- Reduce risk of hepatitis: Your risk of getting hepatitis B and C increases through needle sharing and having unprotected sex.
Other esophageal varices prevention strategies are focused on preventing bleeding in people with cirrhosis of the liver. Prescription beta blockers may be effective in preventing bleeding. Your doctor may also recommend esophageal varices banding.
Get care
We help you live well. And we’re here for you in person and online.
